Detecting and Mitigation of LLM Hallucinations
In the context of LLMs, “hallucination” refers to a phenomenon where the model generates text that is incorrect, nonsensical, or not real. Bias refers to the bias learnt during training.
Type of Hallucinations
- Factual Inaccuracies: The LLM produces a statement that is factually incorrect.
- Unsupported Claims: The LLM generates a response that has no basis in the input or context.
- Nonsensical Statements: The LLM produces a response that doesn’t make sense or is unrelated to the context.
- Improbable Scenarios: The LLM generates a response that describes an implausible or highly unlikely event.
Measure Hallucinations
How to detect hallucination issue?
Measure NER
Check if a new named entity (NE) is present in the text != from the ground truth.
Entailment Ratio
#sentences entailed by the reference text / #sentences in the generated outputUse QG
From generated text → generate question → generate new text → compare the responses
USE <subject, relation, object>
Use Information Extraction models to represent the knowledge in a simpler relational tuples such as . They extract such tuples from the generated output and verify them against relation tuples extracted from the source.
Perplexity
Use perplexity to measure the confidence of the model
BERT Score
BERTScore is an automatic evaluation metric for text generation that computes a similarity score for each token in the candidate sentence with each token in the reference sentence.
BERTScore takes 3 mandatory arguments : predictions (a list of string of candidate sentences), references (a list of strings or list of list of strings of reference sentences) and either lang (a string of two letters indicating the language of the sentences.
RAG Score
Using RAG it provides distance score the the reference text.
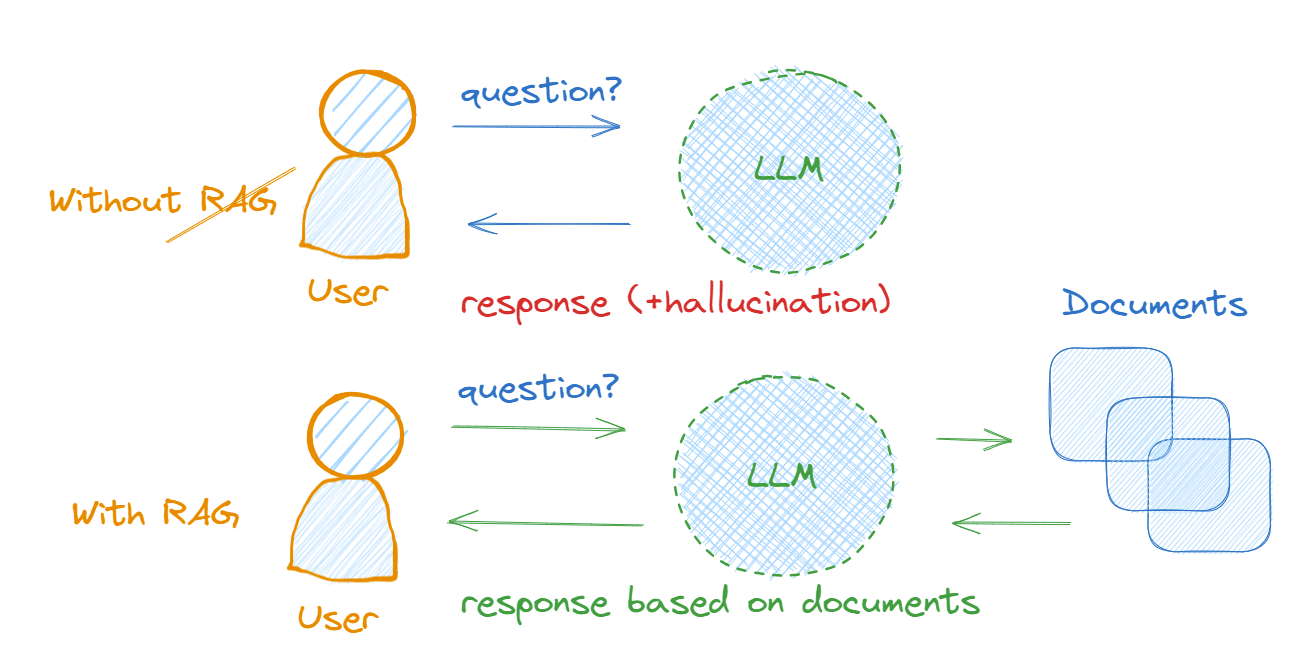
What is RAG?
Mitigate Biases
- More humans to prepare data
- Data Cleaning
Mitigate Hallucination
Reduce length of generated text
Keep simpler.
Temperature
The temperature parameter is a hyperparameter that can be used to control the randomness and creativity of the generated text in a generative language model. It is used to adjust the probabilities of the predicted words in the softmax output layer of the model.
The temperature is also a way for the AI tool to make up things. A lower temperature can create easily predictable answers and a lack of creativity. Yet, a higher temperature increases the randomness of its results.
So if you don’t want to encounter AI hallucinations, adjust the temperature before generating any response.
TOP P
Top p, also known as nucleus sampling, is another hyperparameter that controls the randomness of language model output.
It sets a threshold probability and selects the top tokens whose cumulative probability exceeds the threshold. The model then randomly samples from this set of tokens to generate output. This method can produce more diverse and interesting output than traditional methods that randomly sample the entire vocabulary.
For example, if you set top p to 0.9, the model will only consider the most likely words that make up 90% of the probability mass.
Prompting
Optimize prompting to reduce hallucination. If you can.
RAG
RAG Fact Check
The ideal way to make LLMs learn about personal documents and reduce hallucinations is to augment the LLMs with retrieved documents from knowledge bases. RAG stands for Retrieval Augmented Generation. RAG is used to augment LLM with information from knowledge bases from custom documents.
Embeddings are numerical representations of text data in high-dimensional vector space. Embeddings capture the semantic meaning of texts.
Users employ Vector Databases as knowledge bases, utilizing various indexing algorithms to organize high-dimensional vectors, enabling fast and robust querying ability.
- Llama Index provides in-built tools and methods to build production-grade RAG-based applications.*
Simpler RAG
Langchian
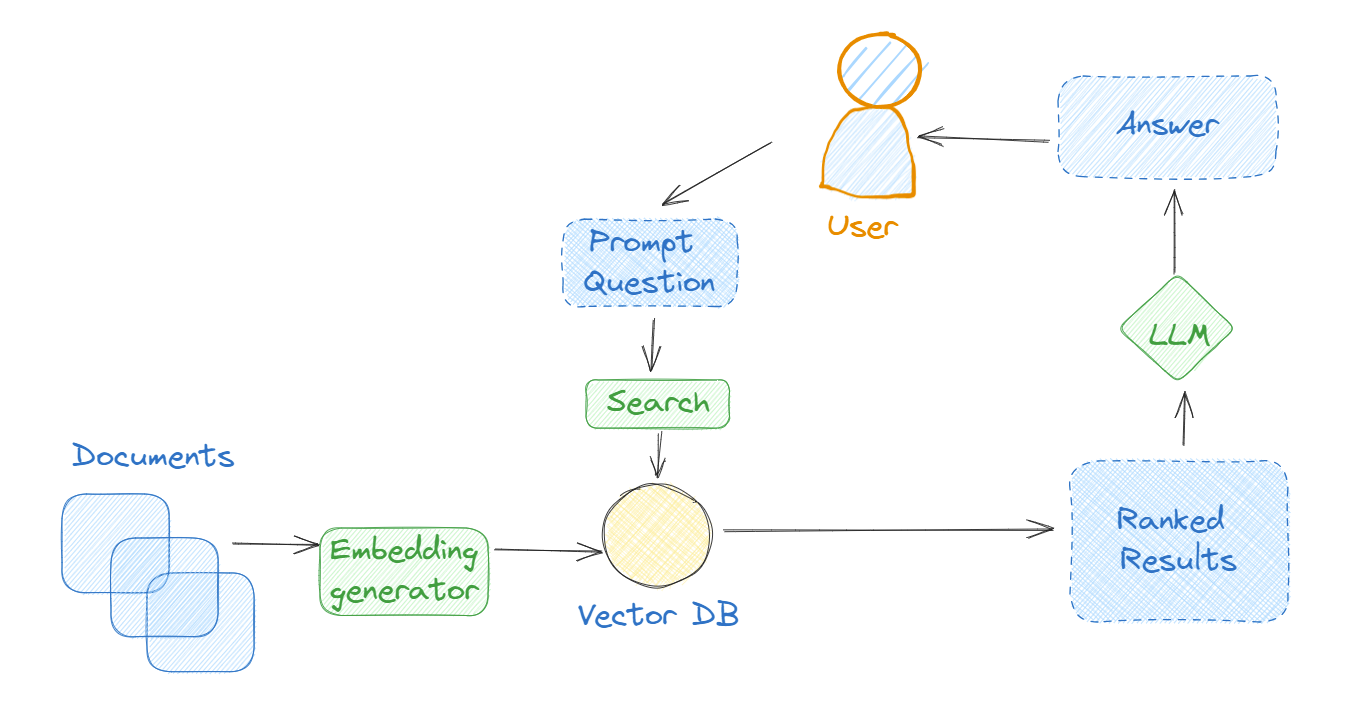
Besides, in a domain-specific QA app, only a few documents contain relevant context per query. So, we need a unified system that streamlines document extraction to answer generation and all the processes between them. This process is called Retrieval Augmented Generation.
-
Documents are converted into a vector representation, often referred to as an embedding. This can be done using different techniques like TF-IDF (Term Frequency-Inverse Document Frequency), Word2Vec, FastText, or more advanced methods like BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) or other transformer-based models. Security data is used in this example.
-
Embeddings (vectorized documents) are stored in a vector database such as Chroma DB or Pinecone. Again, embeddings are numerical representations of the text data, enabling their storage and retrieval in a way that’s optimized for performance.
-
The user asks a question.
-
Once the data is stored in the database, Langchain supports various retrieval algorithms. These include basic semantic search, parent document retriever, self-query retriever, ensemble retriever, and more.
-
When conducting a search, the retrieval system assigns a score or ranking to each document based on its relevance to the query. The documents are then sorted in descending order, with the most relevant documents appearing at the top of the list. This ranking allows the system to quickly identify and access the most relevant information based on their search query. The ranking algorithm takes into account several factors such as keyword matching, document popularity, user behavior, and other relevance signals to determine the order of the results.
-
Results are sent to the LLM (e.g., GPT, Falcon, LLaMA2, etc.).
-
Leveraging the contextual representation, the model then generates a response.
Generative AI, Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG), and Langchain
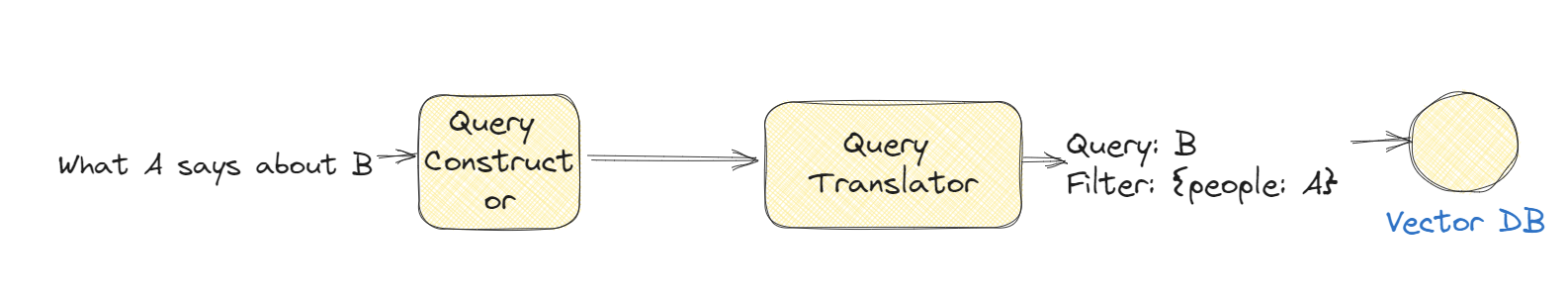
Self query
Use self query:
Fine Tune on High performance data
Perform fine tuning on high perf data.
Reinforcement Learning with AI feedback (RLAIF)
Constitutional AI feedback given by another model overfitted on corpus.